Last update: 2021.04.02
Backup! Backup! Backup!
I have two r-pi booting from SSD drives instead of SD cards. Now, I want to triger rsync from r-pi A and have both r-pi A and r-pi B (the full SSD boot drive) copied on an external NAT drive connected to r-pi A.
For this project, I will use rsnapshot to make automated periodic copies.
Step 1: multiple sshd instance
When I need access to the r-pi from my laptop or my mobile phone, I connect through ssh with a rsa key secured by a strong password. For this project, we need to allow r-pi A to connect to r-pi B through ssh, but we will use another sshd instance and connect using a rsa key without password.
First, let’s create a secondary sshd instance to open a connection between r-pi A and B.
- On the r-pi B -
Change directory
cd /etc/ssh
Copy the sshd_config file as sshd-internal_config or using whatever name you like
sudo cp sshd_config sshd-internal_config
Edit sshd-internal_config
sudo nano sshd-internal_config
Change the port number (22555 is an example). Just make it different than the default port (usually 22) or any other port already in use.
Port 22555
Change directory
cd /lib/systemd/system
Copy the ssh.service file as ssh-internal.service or using whatever name you like
sudo cp ssh.service ssh-internal.service
Edit ssh-internal.service
sudo nano ssh-internal.service
Add the following
[Unit]
Description=OpenBSD Secure Shell server
After=network.target auditd.service
ConditionPathExists=!/etc/ssh/sshd_not_to_be_run
[Service]
EnvironmentFile=-/etc/default/ssh
PIDFile=/var/run/ssh-internal.pid
ExecStart=/usr/sbin/sshd -D -f /etc/ssh/sshd-internal_config $SSHD_OPTS
ExecReload=/bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID
KillMode=process
Restart=on-failure
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Alias=<strong>sshd-internal.service</strong>
Enable ssh-internal.service
sudo systemctl enable ssh-internal.service
You should see the following
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/sshd-internal.service to /lib/systemd/system/ssh-internal.service.
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/ssh-internal.service to /lib/systemd/system/ssh-internal.service.
Reboot
sudo reboot
And make sure everything is running normally
sudo systemctl status ssh-internal.service
You should see something like
Active: active (running) since Thu 2021-04-01 02:39:06 CEST; 19h ago
Main PID: 1760 (sshd)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 4915)
CGroup: /system.slice/ssh-internal.service
└─1760 /usr/sbin/sshd -D -f /etc/ssh/sshd-internal_config
- On the r-pi A -
If necessary, create a .ssh directory
sudo mkdir ~/.ssh
Change directory
cd ~/.ssh
Create a rsa key
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 1024 -f ./pi-squid-rsnapshot-key
Set permissions
sudo chmod 700 ~/.ssh
sudo chmod 600 ~/.ssh/*-rsnapshot-key
Create a new config file
sudo nano ~/.ssh/config
And add the following (adjust as needed)
Host remotehost-rsnapshot-pi-squid
Hostname 192.168.1.xxx
port 22555
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/pi-squid-rsnapshot-key
And in the host config file
sudo nano /etc/hosts
Put a new line at the end
192.168.1.xxx remotehost-rsnapshot-pi-squid
Reboot
And test that you can connect with a simple command line
ssh remotehost-rsnapshot-pi-squid
Reference
https://iotalot.com/2017/03/01/how-to-run-multiple-sshd-instances-on-raspberry-pi/
Step 2: rsnapshot
- On the r-pi A -
Install rsnapshot
sudo apt-get install rsnapshot
Edit the rsnapshot configuration file
sudo nano /etc/rsnapshot.conf
What’s important is (edit as needed, these are my settings)
Important: The rsnapshot config file does not recognise spaces, use tab instead or it will generate an error message.
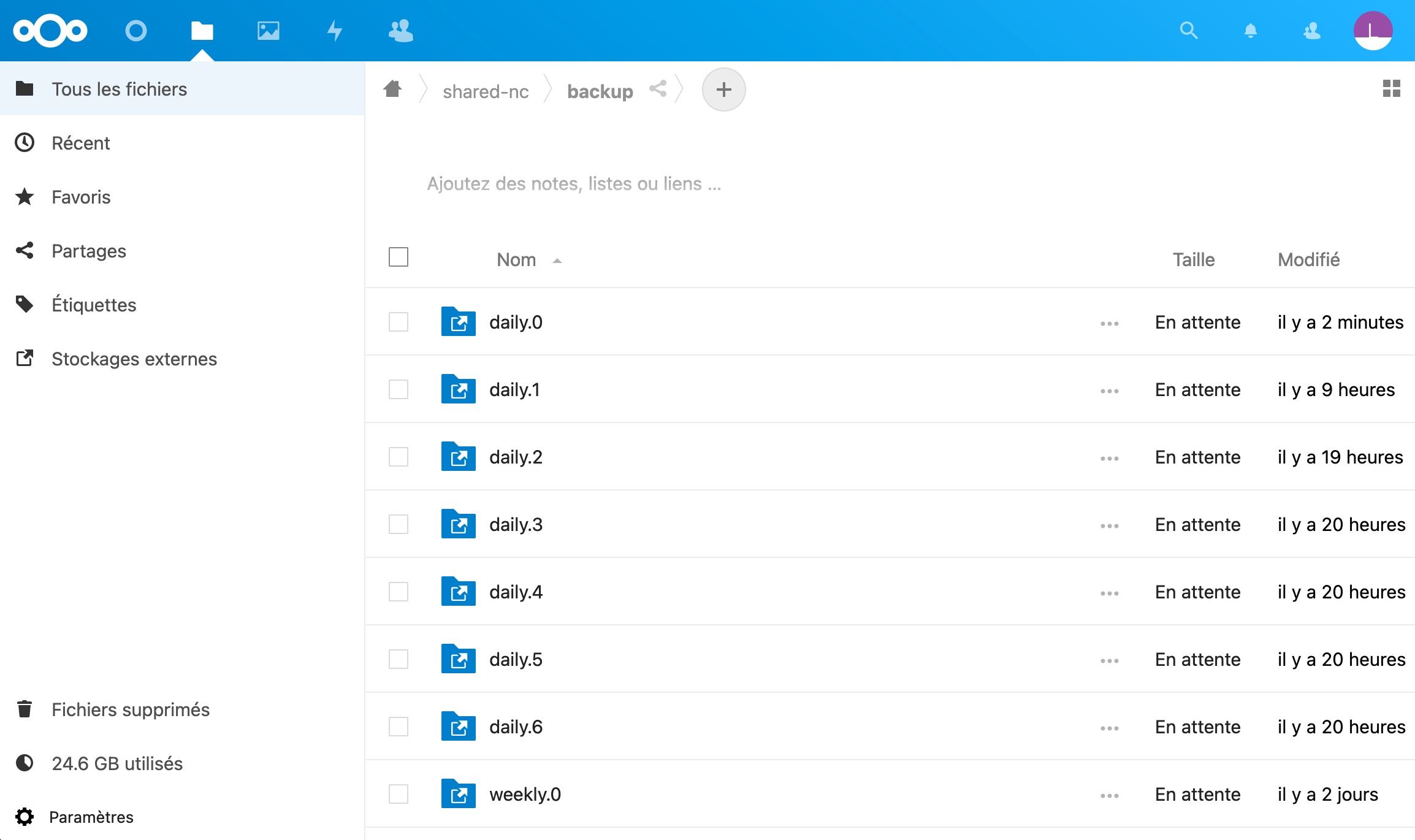
Where you want the backup to be stored
snapshot_root /media/nextcloud/shared/backup/
How many backups do you want on a daily, weekly, monthly basis
retain daily 7
retain weekly 4
retain monthly 12
The arguments to be passed to the command for ssh to work (edit your port number and USER as needed)
ssh_args -p 22555 -i /home/USER/.ssh/pi-squid-rsnapshot-key
Exclude some directories from the copy (again, edit as needed)
exclude /dev/*
exclude /media/*
exclude /proc/*
exclude /sys/*
exclude /run/*
exclude /var/tmp/*
exclude /var/run/*
exclude /tmp/*
exclude /lost+found/*
Define what you want to be backed up. It can be a few selectd directory, or the whole system as below
To backup r-pi A (local)
backup / destination_directory_name/
To backup r-pi B (remote)
backup USER@remotehost-rsnapshot-pi-squid:/ destination_directory_name/
See down below my rsnapshot.con file for reference
Test your configuration syntax
sudo rsnapshot configtest
You should see
Syntax OK
Do a “dry-run” test of the backup process
sudo rsnapshot -v -c /etc/rsnapshot.conf daily
WHen happy, use the cron to schedule your backup processes
Daily: at 1 am
Weekly: every monday at 2 am
Monthly: every first monday of the month at 3 am
0 1 * * * root /usr/bin/rsnapshot daily
0 2 * * 1 root /usr/bin/rsnapshot weekly
0 3 1 * * root /usr/bin/rsnapshot monthly
You can also launch the process manually, with or without the cverbose (-v) argument
sudo rsnapshot -v daily
Tip
If you use Nextcloud, you can install Samba and share your backup directory as a shared folder.
Reference
https://wiki.gentoo.org/wiki/Advanced_backup_using_rsnaphot#Configuration
https://dvpizone.wordpress.com/2014/03/08/using-rsnapshot-with-a-raspberry-pi-to-create-a-backup-device/
https://ubuntu.com/server/docs/tools-rsnapshot
rsnapshot - my full config file
config_version 1.2
snapshot_root /media/nextcloud/shared/backup/
no_create_root 1
cmd_cp /bin/cp
cmd_rm /bin/rm
cmd_rsync /usr/bin/rsync
cmd_ssh /usr/bin/ssh
cmd_logger /usr/bin/logger
cmd_du /usr/bin/du
retain daily 7
retain weekly 4
retain monthly 12
verbose 2
loglevel 3
lockfile /var/run/rsnapshot.pid
ssh_args -p 22555 -i /home/USER/.ssh/pi-squid-rsnapshot-key
one_fs 1
exclude /dev/*
exclude /media/*
exclude /proc/*
exclude /sys/*
exclude /run/*
exclude /var/tmp/*
exclude /var/run/*
exclude /tmp/*
exclude /lost+found/*
backup / mizuki-serv/
backup USER@remotehost-rsnapshot-pi-squid:/ pi-squid/